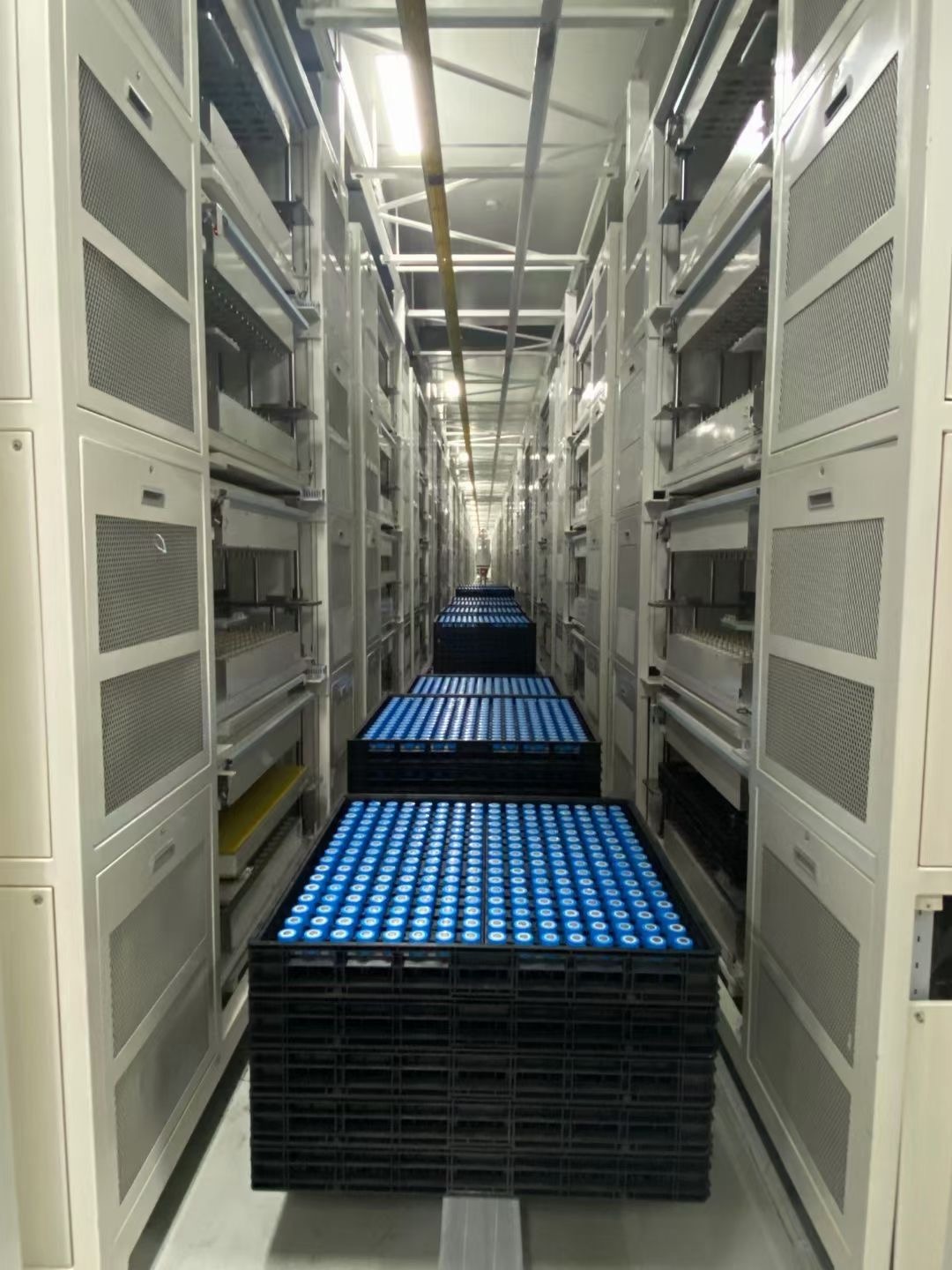
Battery cells form the core of any power bank, playing a pivotal role in determining its performance, lifespan, and safety.
1. Overview of Battery Cell Materials
Battery cells play a pivotal role in the functionality and dependability of power banks. Different materials are used in these cells, each bringing unique attributes to the table.
2. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Battery Cells
What are Lithium-Ion Battery Cells?
Lithium-ion cells are widely used in power banks, known for their high energy density and durability.
Composition:
- Cathode: Typically made from materials like lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese oxide, or lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide.
- Anode: Generally composed of graphite.
- Electrolyte: Consists of lithium salts in organic solvents.
Common Models:
- 18650: A standard size (18mm diameter, 65mm length) offering a good balance between capacity and output.
- 21700: Larger than the 18650 (21mm diameter, 70mm length), providing higher capacity and better efficiency.
Pros:
- High energy density
- Long lifespan
- Low self-discharge
Cons:
- Higher cost
- Safety concerns if mishandled
Applications in Power Banks:
Commonly used in a variety of power banks due to their balance of performance and cost.
3. Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) Battery Cells
What are Lithium Polymer Battery Cells?
Li-Po cells utilize a polymer electrolyte, offering flexibility in form.
Composition:
- Cathode/Anode: Similar to lithium-ion cells.
- Electrolyte: Polymer-based.
Common Models:
- 606090: A rectangular cell (60mm x 60mm x 90mm) known for its high capacity and thin design.
- 1260100: Larger and more capacious, with dimensions of 12mm x 60mm x 100mm, ideal for slim power banks.
Pros:
- Lightweight and versatile
- Safer than Li-ion
- Customizable shapes
Cons:
- More expensive
- Slightly lower energy density
Applications in Power Banks:
Favored for thin, lightweight models.
4. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Battery Cells
What are Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Cells?
Known for thermal stability and safety, LiFePO4 cells are reliable and long-lasting.
Composition:
- Cathode: Lithium iron phosphate.
- Anode: Graphite.
- Electrolyte: Similar to other lithium-based batteries.
Common Models:
- 26650: A cell with a 26mm diameter and 65mm length, offering high capacity and stable output.
- 32700: Larger (32mm diameter, 70mm length), with greater capacity and durability.
Pros:
- Excellent safety and thermal stability
- Long cycle life
- Good high-temperature performance
Cons:
- Lower energy density
- More expensive
Applications in Power Banks:
Ideal for high-capacity, heavy-duty power banks.
5. Emerging Battery Technologies
Graphene Battery Cells
Graphene batteries offer high conductivity and rapid charging potential.
Pros:
- Superior conductivity
- Fast charging
- High durability
Cons:
- Still under development
- High production costs
Solid-State Battery Cells
These replace liquid electrolytes with solid ones, enhancing energy density and safety.
Pros:
- Higher energy density
- Improved safety
- Longer lifespan
Cons:
- Technological challenges
- High initial costs
Zinc-Air Battery Cells
Using air as a reactant, these batteries provide high energy density at a lower cost.
Pros:
- High energy density
- Cost-effective
- Environmentally friendly
Cons:
- Limited recharging
- Complex air management
6. Conclusion
The type of battery cell material and model in a power bank greatly affects its performance, safety, and price. Lithium-ion and lithium polymer cells are most common, each with their own benefits. Models like 18650 and 21700 for Li-ion, or 606090 and 1260100 for Li-Po, offer distinct advantages depending on usage. Emerging technologies like graphene and solid-state batteries promise even better performance in the future.
Understanding these battery cell materials and models will help you choose the power bank that best suits your needs.
If you found this guide useful or have any questions, feel free to reach out in the comments below. We’re here to help!